Assay & Application Notes
Streamlined Protein Quantification: Enhancing Speed and Precision with Absorbance 96 Automate seamlessly integrated into Eppendorf epMotion®
In collaboration with Eppendorf SE

Key Highlights
- A comparative assessment of the Absorbance 96 Automate with another benchtop microplate reader unveiled identical reproducibility, sensitivity, and linearity within the dynamic range.
- The on-deck integration of Absorbance 96 Automate with the epMotion® liquid handling system automates the BCA assay, saving users time during experiments.
- Integrating the Absorbance 96 Automate into an automated workflow enables direct plate reading without requiring user intervention.
Introduction
The quantification of protein concentration in aqueous samples is a vital assay routinely performed in numerous laboratories, encompassing fundamental to clinical research applications. Protein quantification is a crucial first step required for the subsequent processing of protein samples, involving their isolation, separation, and analysis. Depending upon the required accuracy, sensitivity, and purity of the protein samples, various methods can be employed to measure protein concentration, utilizing different detection techniques – colorimetric and fluorometric determination. (1) Given the growing demand for high-throughput protein quantification in diverse fields like drug discovery, proteomics, and therapeutics, lab automation workflows for protein quantification become more crucial. Automated lab processes enhance experiments' reliability, efficiency, and throughput while reducing the likelihood of manual errors. Thus, automatizing some of the well-established, commonly used colorimetric and protein-copper chelation methods, such as Bradford (Coomassie), Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA), and Lowry could prove to be advantageous in protein quantification and analysis workflows. (2)
In this collaborative study with Eppendorf, we present an automated BCA assay enabled by Absorbance 96 Automate, a microplate reader integrated into the deck on the epMotion® liquid handling system. First, the performance of Absorbance 96 Automate was evaluated by comparing it with another benchtop microplate reader. The results exhibited identical readouts with similar reproducibility and linearity, thereby affirming the efficacy and sensitivity of the Absorbance 96 Automate in conducting automated protein quantification. Subsequently, a comparative study between manual and automated workflows showcased expedited procedural steps in the automated workflow, resulting in a substantial reduction in the overall time required to perform the entire BCA assay.
Automated BCA Assay Workflow
Protein quantification was carried out using the Pierce™ Microplate BCA Protein Assay Kit from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Following the manufacturer's protocol, an automated workflow was established utilizing the epBlue software and the epMotion® liquid handling system. This automated process was developed to measure absorbance readouts at 562 nm, facilitated by the on-deck integrated Absorbance 96 Automate. First, the Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) standard graph was constructed, incorporating 7 data points in triplicates. Subsequently, the measurement of unknown samples (4 replicates) was performed across four dilution ranges.
Results
Comparable Readout Values and Identical Reproducibility, Sensitivity Demonstrated by Absorbance 96 Automate and GloMax® Discover
In the comparative analysis, the BSA standard curve analysis was performed by measuring the absorbance of the standard protein samples at 562 nm with the Absorbance 96 Automate and at 560 nm with the GloMax® Discover microplate reader (Promega). The results showed comparable optical density (OD) readouts with high correlation (Fig. 1A). Subsequent examination of OD values from unknown protein samples obtained with both devices also revealed similar results (Fig. 1B), with a high correlation (R² = 0.9989) (Fig. 1C). These findings confirm that the Absorbance 96 Automate shows similar reproducibility, sensitivity, and linearity within the dynamic range when compared to the GloMax® Discover.
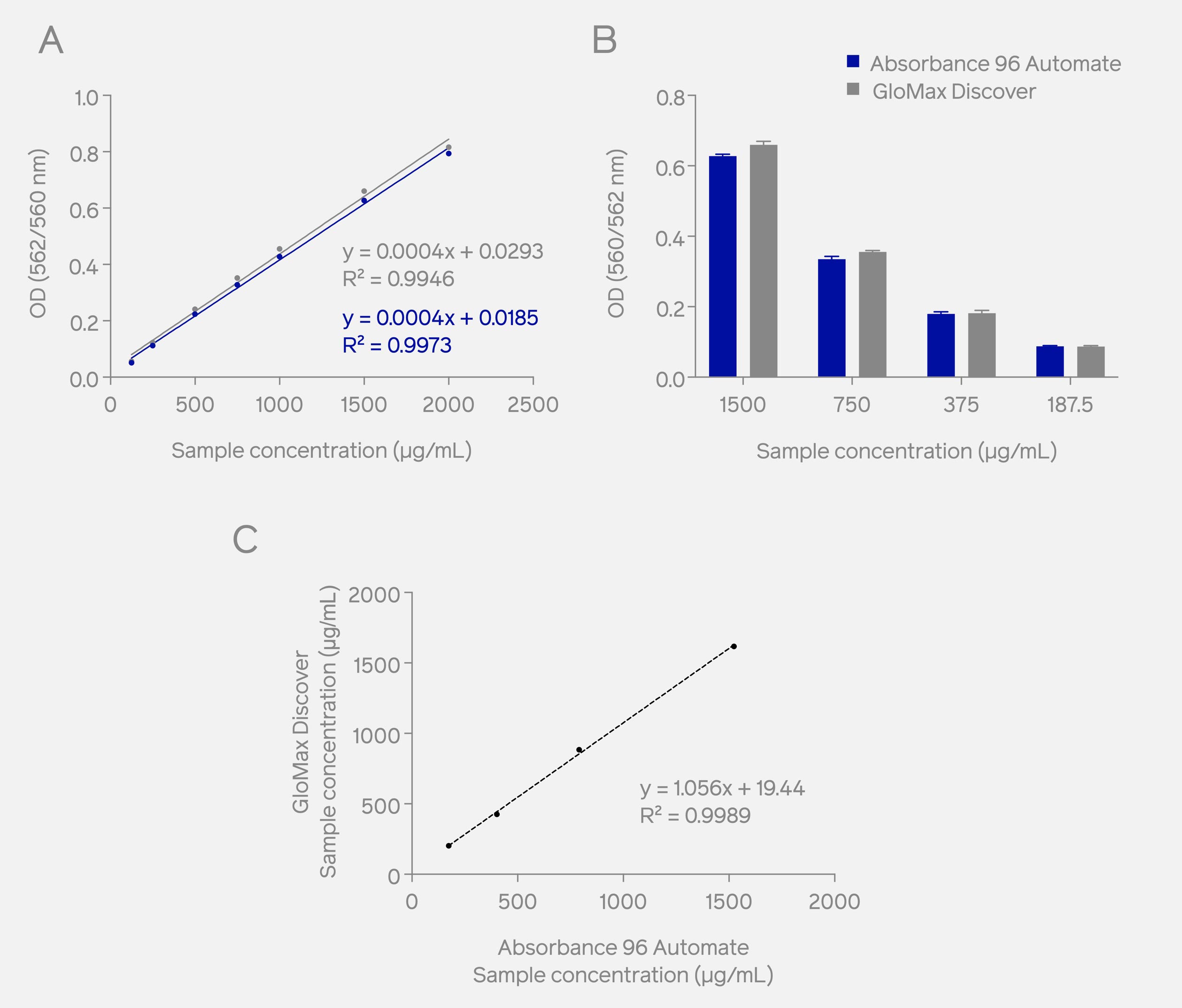
Fig. 1: Comparative analysis utilizing Pierce™ Microplate BCA Protein Assay Kit demonstrates similar OD values (A) for the BSA standard curve and unknown protein samples (B) for the Absorbance 96 Automate (OD measured at 562 nm) and the GloMax® Discover (OD measured at 560 nm). A significant correlation of the sample concentration was observed using both devices (C).
Additionally, it is important to highlight that the Absorbance 96 Automate demonstrated a shorter readout time (2 seconds) than the GloMax® Discover (52 seconds), emphasizing its efficiency in expediting rapid data acquisition.
Enhanced Efficiency and Time Savings Achieved Through Automated Protein Analysis Workflow
A comparative analysis was undertaken to assess the advantage of automated workflow in BCA assay workflow by applying both automated and manual methods. The results exhibited a substantial correlation of the sample concentration between the two methods (Fig. 2), validating the efficient performance of the automated workflow in comparison to the manual approach.
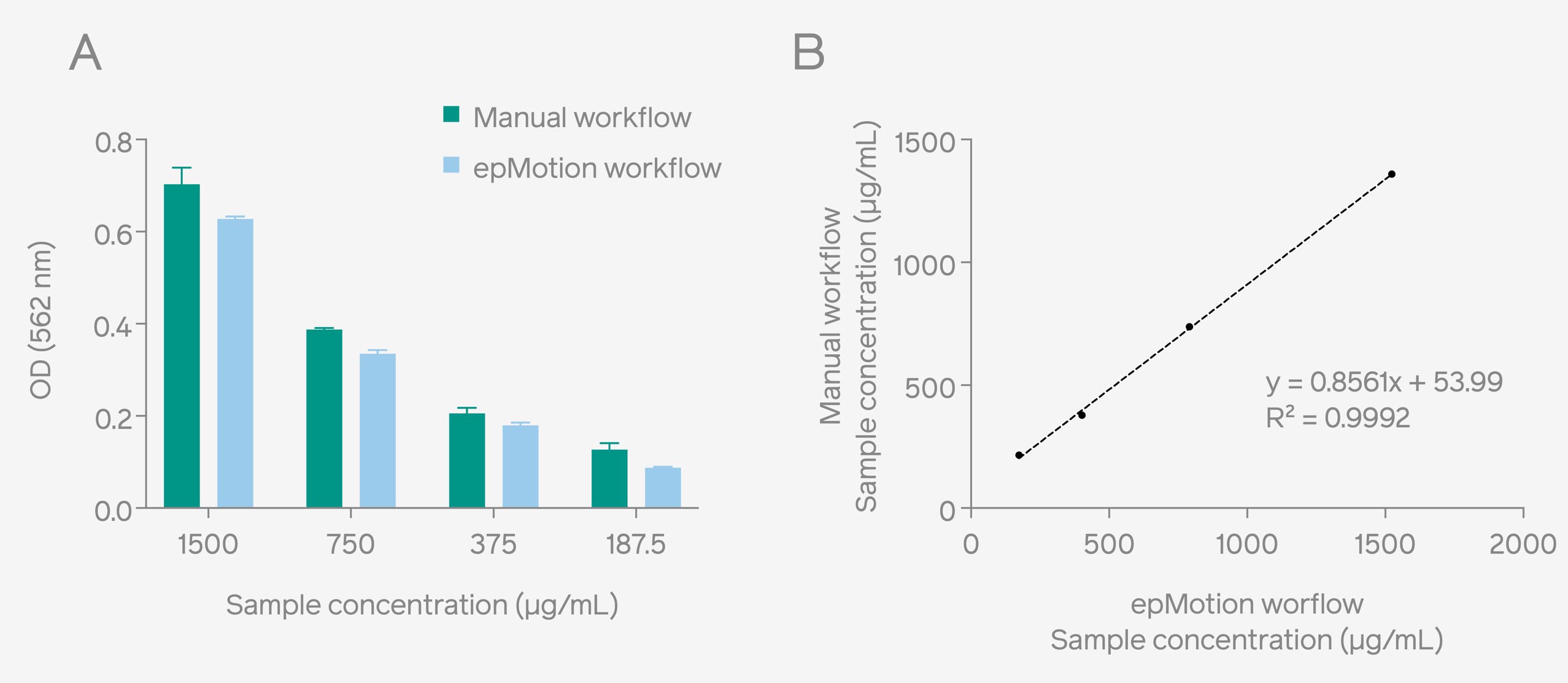
Fig. 2: OD readouts of unknown protein samples obtained through the epMotion® and manual workflow using Pierce™ Microplate BCA Protein Assay Kit (A). A comparison shows a strong correlation of the sample concentration between both methods (B).
Notably, when compared to the manual workflow (90 minutes), the automated workflow (71 minutes) had a substantial decrease in total analysis time. The automated workflow enabled direct plate reading without user intervention, optimizing and saving user time during the execution of the BCA assay.
Summary
The outcomes derived from the comparative study between the Absorbance 96 Automate and the GloMax® Discover microplate reader confirm the efficacy of the Absorbance 96 Automate in conducting the BCA assay, demonstrating comparable readout sensitivity, reproducibility, and linearity. Integrating the Absorbance 96 Automate onto the deck of the epMotion® liquid handling system's deck facilitates enhanced throughput in protein analysis, characterized by increased speed and precision compared to the manual workflow.
References
1. Noble JE. and Bailey MJA. Chapter 8 Quantitation of Protein’, Methods in Enzymology 2019, 463(C), pp. 73–95.
2. Brady PN and Macnaughtan MA. Evaluation of Colorimetric Assays for Analyzing Reductively Methylated Proteins: Biases and Mechanistic Insights’, Analytical biochemistry 2015, 491, p. 43.